什么是链表
单链表是表示一系列节点的数据结构,其中每个节点指向链表中的下一个节点。 相反,双向链表具有指向其前后元素的节点。
与数组不同,链表不提供对链表表中特定索引访问。 因此,如果需要链表表中的第三个元素,则必须遍历第一个和第二个节点才能到得到它。
链表的一个好处是能够在固定的时间内从链表的开头和结尾添加和删除项。
这些都是在技术面试中经常被问到的数据结构,所以让我们开始吧。
另外,可以对链表进行排序。 这意味着当每个节点添加到链表中时,它将被放置在相对于其他节点的适当位置。
节点
链表只是一系列节点,所以让我们从 Node 对象开始。
一个节点有两条信息
指向链表中下一项的指针或引用(对于单链表)
节点的值
对于我们的节点,我们只需要创建一个函数,该函数接受一个值,并返回一个具有上面两个信息的对象:指向下一个节点的指针和该节点的值。
注意,我们可以只声明
value而不是value: value。这是因为变量名称相同(ES6 语法)
节点链表
现在,让我们深入研究 NodeList 类,以下就是节点链表样子。
节点链表将包含五个方法:
push(value): 将值添加到链表的末尾
pop() :弹出链表中的最后一个值
get(index):返回给定索引中的项
delete(index):从给定索引中删除项
isEmpty(): 返回一个布尔值,指示链表是否为空
printList():不是链表的原生方法,它将打印出我们的链表,主要用于调试
构造函数
构造函数中需要三个信息:
head:对链表开头节点的引用
tail:对链表末尾节点的引用
length:链表中有多少节点
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
}
IsEmpty
isEmpty() 方法是一个帮助函数,如果链表为空,则返回true。
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}printList
这个实用程序方法用于打印链表中的节点,仅用于调试目的。
printList () {
const nodes = [];
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
nodes.push(current.value);
current = current.next;
}
return nodes.join(' -> ');
}Push
在添加新节点之前,push 方法需要检查链表是否为空。如何知道链表是否为空? 两种方式:
isEmpty()方法返回true(链表的长度为零)head指针为空
对于这个例子,我们使用 head是否为null来判断链表是否为空。
如果链表中没有项,我们可以简单地将head 指针和tail指针都设置为新节点并更新链表的长度。
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
this.length++;
return node;
}如果链表不是空的,我们必须执行以下操作:
将
tail.next指向新节点将
tail指向新节点更新链表长度
以下是完整的 push 方法:
push(value) {
const node = Node(value);
// The list is empty
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
this.length++;
return node;
}
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
this.length++;
}Pop
在删除链表中的最后一项之前,我们的pop方法需要检查以下两项内容:
检查链表是否为空
检查链表中是否只有一项
可以使用isEmpty方法检查链表是否包含节点。
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
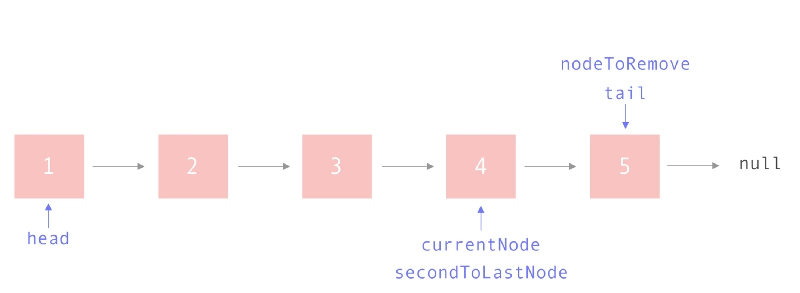
}我们如何知道链表中只有一个节点? 如果 head 和tail 指向同一个节点。但是在这种情况下我们需要做什么呢? 删除唯一的节点意味着我们实际上要重新设置链表。
if (this.head === this.tail) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length--;
return nodeToRemove;
}如果链表中有多个元素,我们可以执行以下操作
当链表中有节点时, 如果链表中的下一个节点是 tail 更新 tail 指向当前节点 当前节点设置为 null, 更新链表的长度 返回前一个 tail 元素
它看起来像这样:
1 let currentNode = this.head;
2 let secondToLastNode;
3
4 //从前面开始并迭代直到找到倒数第二个节点
5
6 while (currentNode) {
7 if (currentNode.next === this.tail) {
8 // 将第二个节点的指针移动到最后一个节点
9 secondToLastNode = currentNode;
10 break;
11 }
12 currentNode = currentNode.next;
13 }
14 // 弹出该节点
15 secondToLastNode.next = null;
16 // 将 tail 移动到倒数第二个节点
17 this.tail = secondToLastNode;
18 this.length--;
19
20 // 初始化 this.tail
21 return nodeToRemove;如果你无法想象这一点,那么让我们来看看它。
第6-10行:如果链表中的下一个节点是最后一个项,那么这个当前项目就是新tail,因此我们需要保存它的引用。
if (currentNode.next === this.tail) {
secondToLastNode = currentNode;
}第15行:将secondToLastNode更新为null,这是从链表中“弹出”最后一个元素的行为。
secondToLastNode.next = null;
第17行:更新tail以指向secondToLastNode。
this.tail = secondToLastNode;
第18行:更新链表的长度,因为我们刚删除了一个节点。
第21行:返回刚刚弹出的节点。
以下是完整的pop方法:
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
const nodeToRemove = this.tail;
// There's only one node!
if (this.head === this.tail) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length--;
return nodeToRemove;
}
let currentNode = this.head;
let secondToLastNode;
// Start at the front and iterate until
// we find the second to last node
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.next === this.tail) {
// Move the pointer for the second to last node
secondToLastNode = currentNode;
break;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// Pop off that node
secondToLastNode.next = null;
// Move the tail to the second to last node
this.tail = secondToLastNode;
this.length--;
// Initialized to this.tail
return nodeToRemove;
}Get
get方法必须检查三种情况:
索引是否超出了链表的范围
链表是否为空
查询第一个元素
如果链表中不存在请求的索引,则返回null。
// Index is outside the bounds of the list
if (index < 0 || index > this.length) {
return null;
}如果链表为空,则返回null。你可以把这些if语句组合起来,但是为了保持清晰,我把它们分开了。
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}如果我们请求第一个元素,返回 head。
// We're at the head!
if (index === 0 ) {
return this.head;
}否则,我们只是一个一个地遍历链表,直到找到要查找的索引。
let current = this.head;
let iterator = 0;
while (iterator < index) {
iterator++;
current = current.next;
}
return current;以下是完整的get(index)方法:
get(index) {
// Index is outside the bounds of the list
if (index < 0 || index > this.length) {
return null;
}
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
// We're at the head!
if (index === 0 ) {
return this.head;
}
let current = this.head;
let iterator = 0;
while (iterator < index) {
iterator++;
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}Delete
delete方法需要考虑到三个地方
删除的索引超出了链表的范围
链表是否为空
我们想要删除
head
如果链表中不存在我们要删除的索引,则返回 null。
// Index is outside the bounds of the list
if (index < 0 || index > this.length) {
return null;
}如果我们想删除head,将head设置为链表中的下一个值,减小长度,并返回我们刚刚删除的值。
if (index === 0) {
const nodeToDelete = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
this.length--;
return nodeToDelete;
}如果以上都 不是,则删除节点的逻辑如下:
循环遍历正在查找的索引 增加索引值 将前一个和当前指针向上移动一个 将当前值保存为要删除的节点 更新上一个节点的指针以指向下一个节点 如果下一个值为 `null` 将`tail`设置为新的最后一个节点 更新链表长度 返回已删除的节点
如果你需要可视化图片,请参考Pop部分中的图表。
以下是完整的 delete 方法:
delete(index) {
// Index is outside the bounds of the list
if (index < 0 || index > this.length - 1) {
return null;
}
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
if (index === 0) {
const nodeToDelete = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
this.length--;
return nodeToDelete;
}
let current = this.head;
let previous;
let iterator = 0;
while (iterator < index) {
iterator++;
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
const nodeToDelete = current;
// Re-direct pointer to skip the element we're deleting
previous.next = current.next;
// We're at the end
if(previous.next === null) {
this.tail = previous;
}
this.length--;
return nodeToDelete;
}** 原文:https://itnext.io/creating-linked-lists-in-javascript-2980b0559324**